How AI Vision Systems Work in Order Picking | Digital Fractal
AI vision systems are transforming warehouse order picking by combining computer vision, machine learning, and real-time data processing. These systems identify, verify, and track items with up to 99% accuracy, significantly reducing errors and improving efficiency. They integrate with existing warehouse tools to streamline operations, handle diverse inventories, and minimize manual labour. Here’s what you need to know:
- Key Features: AI vision systems use cameras, sensors, and algorithms to identify items, check quality, and guide robotic arms or workers.
- Performance: Capable of up to 1,400 picks/hour, reducing picking times by 23% and improving inventory accuracy by 35%.
- Hardware: Includes 2D/3D cameras, robotic arms, and barcode scanners for precise item handling.
- Software: Real-time data processing ensures instant decision-making, while machine learning optimizes operations over time.
- Benefits: Lower costs, reduced errors, and improved worker safety.
- Challenges: High initial costs, integration complexity, and compliance with Canadian privacy laws.
For Canadian warehouses, companies like Digital Fractal Technologies Inc. offer tailored solutions, including readiness audits, to ensure smooth adoption of AI vision systems while addressing regulatory and operational needs.
Demo of AI robots for order picking (fully automated warehouse) | Brightpick
Core Technologies and Components of AI Vision Systems
AI vision systems are at the heart of modern warehouse automation, driving efficiency in order picking by converting visual data into precise actions. These systems rely on three interconnected layers – software, hardware, and data processing – that work together to meet the performance demands of today’s warehouses.
Computer Vision Algorithms
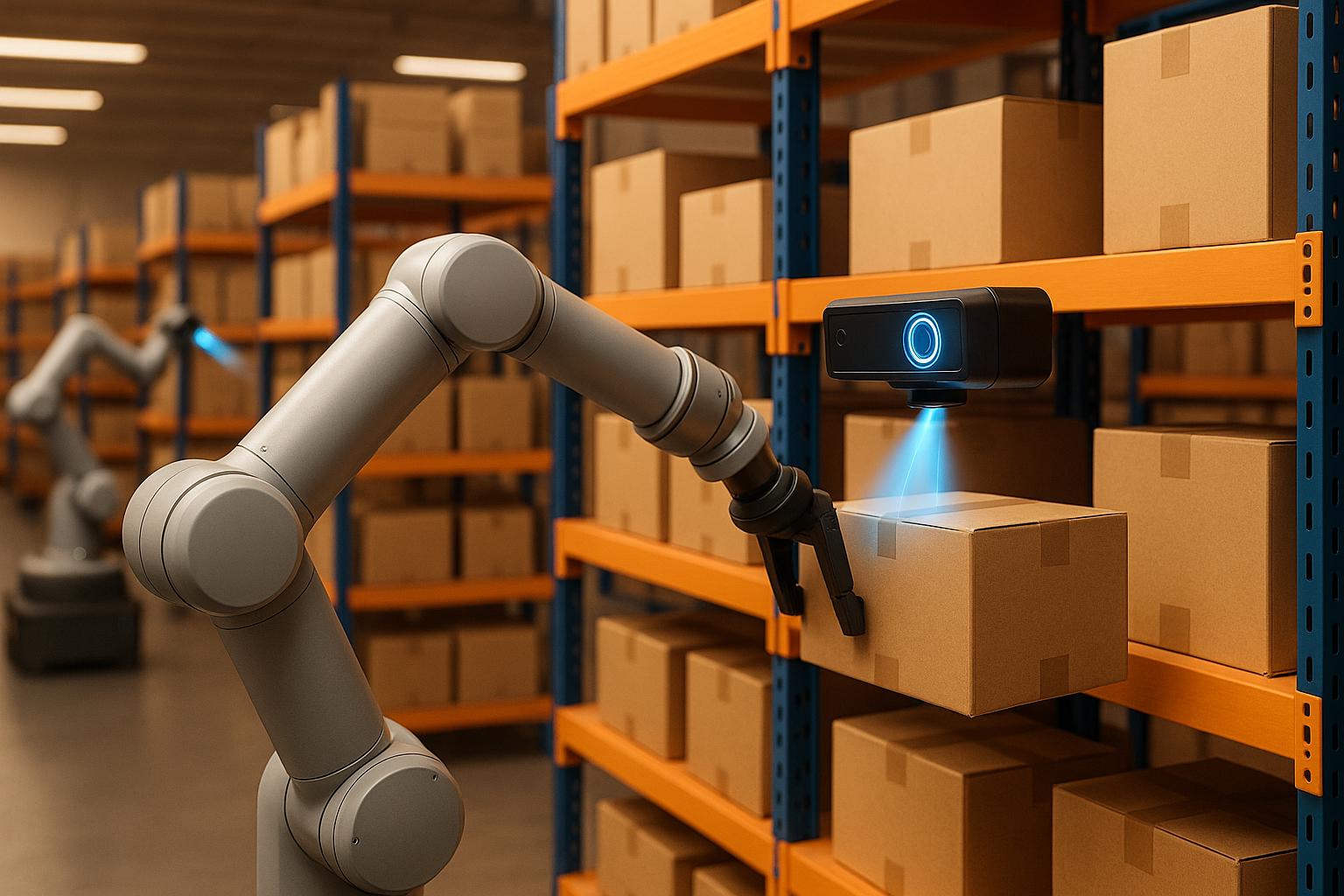
Computer vision algorithms are the brains behind AI vision systems, enabling machines to interpret and act on visual data. At the core are object detection algorithms, which continuously scan the warehouse to identify and locate items within the camera’s field of view. These algorithms ensure every product’s position on shelves or in bins is accurately tracked.
Classification algorithms take this a step further by categorizing items based on attributes like type, size, weight, and texture. Unlike older systems that required uniform packaging, these advanced systems can recognize a variety of shapes and materials, making them suitable for warehouses with diverse inventories.
Tracking algorithms keep tabs on items as they move through the picking process. Whether a robotic arm is retrieving an item or an operator is handling it, the system monitors every movement to ensure precision and prevent errors. Together, these algorithms perform a seamless workflow of detecting, classifying, and tracking items. Over time, machine learning refines this process by analysing historical data, boosting both speed and accuracy.
Hardware Components
The physical components of AI vision systems are designed to capture, process, and act on visual data with precision. Multiple cameras, often mounted above robotic arms or placed strategically in picking areas, gather essential visual information. These cameras include both 2D and 3D imaging capabilities, with 3D systems providing critical depth perception for tasks like locating items or navigating cluttered spaces.
Stereo vision systems, which use multiple cameras to create three-dimensional images, are particularly useful for robotic arms operating in complex environments. These systems allow robots to navigate around obstacles and retrieve items from crowded or partially obscured bins.
Robotic arms equipped with suction cups or grippers carry out the physical task of picking items. These arms rely on calibration patterns to correct positioning errors in real-time, ensuring accuracy even after thousands of cycles. To complement these systems, real-time sensors and barcode scanners verify product information and detect defects before items leave the warehouse. This integrated hardware setup allows robots to autonomously navigate aisles and adapt their paths while maintaining high levels of precision.
Real-Time Data Processing
Real-time data processing is the final piece of the puzzle, transforming raw visual data into actionable instructions almost instantly. Images captured by cameras are analysed within milliseconds to identify, verify, and match items with orders. This rapid analysis enables robotic systems to make split-second decisions about navigation, selection, and placement.
Edge computing is a game-changer here, processing data locally on warehouse devices instead of relying on distant servers. This reduces latency and ensures immediate responsiveness, which is especially critical when robotic arms need to adjust their movements in real time.
Machine learning models enhance this process by identifying patterns in the data stream, optimising picking routes, and reducing travel time. With real-time visual confirmation at every step – whether it’s item identification, verification, or quality control – errors are caught and corrected on the spot, rather than later in the fulfilment process.
For example, a Swedish automotive manufacturer successfully implemented AI-enabled vision systems to tackle challenges like part searching, quality control, and material replenishment. This upgrade improved task efficiency and streamlined operations. The results speak volumes: AI-driven systems have reduced average picking times by 23% through smarter storage location assignments. Thanks to real-time processing, these performance gains remain consistent even during extended operational hours.
How AI Vision Systems Work in Order Picking: Step-by-Step Process
AI vision systems are reshaping warehouse operations with a structured, three-stage process that combines advanced computer vision and real-time decision-making. Each stage builds on the last, creating a streamlined workflow that boosts both speed and accuracy in order fulfillment.
Item Identification and Location
Cameras installed above picking stations scan shelves to identify items using factors like shape, size, colour, and packaging design. By incorporating barcode or QR code scanning alongside advanced pattern recognition, the system ensures items are matched accurately to order requirements.
This level of precision is especially important in Canadian warehouses, where small variations in components can make a big difference. For example, in automotive parts warehouses, the system can differentiate between nearly identical engine parts or fasteners, reducing the risk of costly assembly line delays.
The system also calculates the exact coordinates of each item and determines the best approach angles for retrieval. This capability allows it to navigate around obstacles and retrieve items from tight spots without disturbing nearby inventory. Once the item is located, the system immediately initiates verification.
Verification and Quality Control
Before picking, the AI vision system performs thorough verification to catch errors early in the process.
SKU verification ensures that the visual identification matches the order requirements. It checks the SKU, counts the items, and assesses their condition. In pharmaceutical distribution centres across Canada, this step is critical. The system can detect damaged packaging or incorrect quantities, preventing errors that could affect patient safety or lead to expensive returns.
Another key aspect is condition assessment. The system scans for visible damage such as dents, tears, or other defects. In food logistics, for instance, AI vision can identify produce showing signs of spoilage or damaged packaging, helping maintain quality throughout the supply chain.
For time-sensitive products, the system also checks expiry dates. By reading and interpreting date stamps, it flags items nearing expiration. This feature is invaluable for Canadian retailers managing perishable goods over long distances, ensuring freshness upon delivery.
Guidance for Robotic Arms or Operators
Once verification is complete, the system guides the picking process with precision. It calculates the best grip positions and approach angles, sending continuous updates to robotic arms as they move toward the target. In Canadian food logistics, vision-guided robots can handle fragile items like produce, adjusting their grip strength based on visual feedback.
For human operators, AI vision systems provide on-screen guidance. Displays highlight the correct items with bright overlays, suggest optimal picking paths, and offer real-time feedback on task progress. This reduces errors and integrates smoothly into natural workflows.
The system also optimizes paths by analysing inventory locations and pending orders to recommend the fastest picking routes. This not only cuts down on travel time but also reduces physical strain on workers, especially during busy periods.
Real-time error correction is another standout feature. If the wrong item is picked, the system immediately detects the mistake and provides corrective instructions. This instant feedback ensures mistakes don’t propagate through the fulfillment process.
In controlled studies, these AI-powered systems have shown impressive results. They’ve reduced average order picking times by 23% through smarter storage location assignments, while maintaining up to 1,400 picks per hour with an accuracy rate of 99%.
sbb-itb-fd1fcab
Benefits and Challenges of Vision-Based Order Picking
AI vision systems bring impressive accuracy and speed to order picking, but they also require thoughtful investment and planning. Below, we break down the key benefits and challenges of adopting these systems in Canadian warehouses.
Benefits
AI vision systems excel in accuracy and speed, achieving up to 99% picking accuracy and handling as many as 1,400 picks per hour. This drastically reduces errors and returns, leading to happier customers across Canada’s diverse retail sector.
They also contribute to lower costs. By integrating AI with labour management systems, warehouses in Canada can cut logistics expenses by 15%. At the same time, inventory accuracy can improve by 35%, and service levels can jump by 65%.
Another advantage is better worker well-being. Automating repetitive and physically demanding tasks – like reaching, bending, and lifting – reduces strain on employees. This allows staff to focus on more complex and rewarding work while lowering the risk of musculoskeletal disorders.
AI systems also offer continuous learning capabilities. Using machine learning, these systems analyse past data to refine picking processes, optimize routes, and improve accuracy over time. Even better, when one robot learns something new, that knowledge can be shared across the entire fleet, enhancing the operation as a whole.
Challenges
Despite the benefits, there are hurdles to overcome. High initial costs are a significant barrier. Implementing these systems requires a considerable investment in hardware, software, integration, and infrastructure updates. While the long-term savings are clear, the upfront expense can be tough for some warehouses to justify.
Integration complexity is another challenge. Fully automated order fulfilment relies on seamless coordination between various systems, including goods-to-person solutions, pick-and-place robots, AI vision technology, and warehouse execution systems. Customizing existing systems to work with AI platforms often requires significant technical expertise.
Privacy and data protection concerns are particularly relevant in Canada. AI vision systems collect extensive data on staff activities, which must be carefully managed to comply with laws like PIPEDA and provincial privacy regulations. This involves clear policies on data collection, storage, and usage, as well as robust security measures.
Lastly, staff training and change management demand time and effort. Workers need thorough training on new systems, and adapting to new workflows can be challenging. Current manual methods of identifying tasks that impact worker well-being are also time-consuming and require specialized expertise.
Comparison Table: Benefits vs Challenges
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Up to 99% accuracy and 1,400 picks/hour | High upfront costs for implementation |
| 15% reduction in logistics costs, 35% better inventory accuracy, 65% higher service levels | Complex integration with existing systems |
| Reduced physical strain on workers | Privacy concerns and compliance with Canadian laws |
| Systems improve over time with machine learning | Extensive training and change management required |
| Knowledge sharing across robot fleets | Ongoing updates and maintenance |
| Faster and more accurate order fulfilment | Need for technical expertise during setup |
| Improved customer satisfaction | Data security and access control challenges |
To succeed with AI vision systems, Canadian warehouses should start with a detailed readiness audit. This involves analysing current processes, identifying opportunities, and addressing risks. A clear roadmap – typically spanning 6 to 12 months – can help ensure a smoother transition and faster results. With proper planning and expert guidance, the shift to AI-powered operations becomes much more achievable.
Implementation Considerations and Best Practices
Introducing AI vision systems into Canadian warehouses can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency, but achieving these benefits requires careful planning. To ensure a smooth deployment, it’s vital to address technical, regulatory, and operational factors. A structured approach is key to integrating these advanced systems into existing infrastructure while meeting both short-term needs and long-term goals.
Infrastructure and Integration
Integrating AI vision systems into current workflows starts with evaluating your warehouse’s existing capabilities and identifying where upgrades are needed. One critical factor is network infrastructure: these systems rely on high-speed networks – preferably gigabit or better – to handle continuous video feeds and real-time AI processing demands. Without sufficient bandwidth, delays can occur, reducing the system’s effectiveness and accuracy.
When it comes to processing, organizations must choose between on-site servers (which can cost between CAD $50,000 and $200,000) or cloud-based solutions that have ongoing expenses. Edge computing offers another option, minimizing latency for real-time decisions, while cloud systems provide scalability. Many Canadian warehouses opt for a hybrid approach, combining the strengths of both.
Another challenge is integrating AI vision platforms with existing warehouse management (WMS) and execution systems (WES). Legacy systems often use outdated data structures or communication protocols, making seamless integration difficult. Middleware or custom integration layers can help bridge these gaps. Pilot testing in specific areas of the warehouse is a smart way to identify potential issues without disrupting overall operations. Opting for systems with open APIs and support for standard communication protocols can also simplify the process.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Canadian warehouses must navigate strict privacy regulations when implementing AI vision systems. Laws such as the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) require organizations to take specific measures when these systems capture video footage of staff.
To comply with privacy laws, consider these five key steps:
- Clearly inform employees about what data is being collected and how it will be used.
- Define strict protocols for data acquisition.
- Restrict access to authorized personnel only.
- Secure stored data with encryption and access controls.
- Develop policies for data retention and breach response.
Conducting privacy impact assessments before deployment is essential. These assessments document compliance efforts and should involve consultation with legal experts familiar with Canadian privacy laws. In some cases, staff consent or union consultations may also be required. Transparent communication about the system’s purpose is crucial to building trust, emphasizing that the technology is intended to improve efficiency rather than monitor employees.
Data residency is another critical factor. Cloud-based systems should use Canadian data centres to ensure compliance with data sovereignty requirements. Establish clear policies for data retention, deletion schedules, and any cross-border data transfers. Since digital maturity varies across Canadian warehouses – ranging from basic systems like QR codes to advanced technologies like automated guided vehicles – privacy measures must be tailored to each facility’s specific needs.
Once regulatory concerns are addressed, organizations can focus on implementing tailored solutions for their digital transformation journey.
Custom Solutions with Digital Fractal Technologies Inc.
Digital Fractal Technologies Inc. offers expertise in helping Canadian businesses navigate the technical and regulatory challenges of implementing AI vision systems. Through custom software development and AI integration, they provide solutions tailored to unique operational needs. Their AI Readiness Audit evaluates existing processes, data, tools, and risks, delivering a detailed 6–12 month roadmap that outlines infrastructure requirements.
Their approach is highly customer-focused. For example, Digital Fractal transformed the operations of a leading Canadian energy service company by moving from manual, paper-based processes to a fully integrated mobile and web system.
"Digital Fractal Technologies was contracted to digitally transform our trucking operations. We are a leading Canadian energy service company in the oil and gas sector and prior to working with Digital Fractal, most of our processes were manual and done by paper. The Xtreme Oilfield mobile application and web backend system that was developed for us digitized our paper forms, automated certificate/permit management, computerized job dispatching, and brought timesheets, vehicle repair, and communications to the field on an iPad."
– Regg. M, Operations
Digital Fractal’s AI solutions streamline workflows by automating repetitive tasks and enhancing operational efficiency. They specialize in image and video processing, ensuring systems meet the specific needs of each warehouse. Their commitment doesn’t end with deployment – they provide ongoing support to optimize systems as machine learning continues to improve performance.
"Since the app’s initial completion we have made several additions and improvements, some with little notice and a tight deadline, and they have been able to deliver what we need."
– James M, CEO
Conclusion: Improving Efficiency with AI Vision Systems
AI vision systems are revolutionizing the way Canadian warehouses manage item verification and order picking. By turning manual processes into intelligent, automated workflows, these systems achieve impressive results, including up to 99.9% picking accuracy, while cutting down on labour costs and processing times. This technology is a game-changer for businesses facing challenges like rising labour expenses and growing demands for faster, error-free deliveries.
Warehouses adopting AI vision systems see notable improvements in operations, thanks to real-time data processing that scales effortlessly to handle larger volumes without compromising precision. This capability is especially important in industries such as pharmaceuticals and electronics, where visual confirmation is essential. The shift to automation not only improves efficiency but also lays the groundwork for sustained advancements across warehouse environments.
These systems go beyond enhancing accuracy – they also promote worker safety and support scalable operations. Unlike traditional manual methods prone to human error, AI vision systems use computer vision and machine learning to continually refine picking routes, driving error rates to near zero. Importantly, this technology doesn’t replace workers but instead supports them, creating safer and more productive workplaces.
For warehouses ready to modernize, Digital Fractal Technologies Inc. brings valuable expertise. With extensive experience in AI consulting and custom development across both public and private sectors, they ensure solutions meet Canadian regulatory and operational standards. Their AI Readiness Audit provides businesses with a clear 6–12 month roadmap, pinpointing areas where automation can have the most impact.
Their expertise is backed by a strong track record. For instance, their work with Xtreme Oilfield demonstrates how digital transformation can overhaul manual, paper-based processes, creating integrated systems that enhance operations. This same expertise applies to warehouse settings, where AI vision systems can automate repetitive tasks and streamline workflows.
The success of these systems depends on partnering with experts who understand both the technical challenges and the Canadian regulatory landscape. Digital Fractal Technologies Inc. specializes in custom solutions that seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure while addressing privacy compliance, data residency, and local operational needs. Their commitment to ongoing support ensures businesses can continually refine their systems as machine learning evolves.
FAQs
How do AI vision systems enhance accuracy and efficiency in order picking?
AI vision systems are transforming the way order picking is done by leveraging cutting-edge technologies like computer vision and machine learning. These systems can identify, locate, and classify items in real-time, making the process faster while cutting down on mistakes.
By automating repetitive tasks and ensuring accurate item selection, businesses can boost productivity and reduce errors. This not only streamlines operations but also improves customer satisfaction with quicker and more precise order fulfilment.
What steps should Canadian warehouses take to implement AI vision systems while adhering to privacy regulations?
To bring AI vision systems into Canadian warehouses, the first step is to evaluate your specific operational needs. Identify key areas where AI could make a difference – think inventory tracking or streamlining order picking. Once you’ve pinpointed these opportunities, it’s crucial to ensure compliance with Canadian privacy laws, particularly the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA). Protecting employee and customer data should be a top priority, which means using strict access controls and, when needed, anonymizing sensitive information.
Partnering with experts is another vital step. Companies like Digital Fractal Technologies Inc. specialize in creating and implementing AI-driven solutions tailored to your business. They can help you navigate both the technical and regulatory landscapes, making the transition to advanced AI systems smooth and compliant.
What challenges do warehouses face when adopting AI vision systems for order picking, and how can these be resolved?
Warehouses shifting to AI vision systems for order picking often face hurdles like steep initial costs, blending the technology into existing workflows, and ensuring employees are adequately trained. These systems demand a hefty investment in hardware and software, along with meticulous planning to integrate them smoothly into current operations.
To navigate these obstacles, businesses can begin with a detailed cost-benefit analysis to validate the investment. A phased rollout can help reduce disruptions, while thorough training programs equip staff to embrace the new technology effectively. Consistent technical support also plays a key role in maintaining seamless operations. Collaborating with specialists like Digital Fractal Technologies Inc can simplify the process by delivering customized solutions tailored to the unique needs of the business.