How to Add Automated Testing to CI/CD Pipelines | Digital Fractal
Automated testing is essential for making CI/CD pipelines faster and more reliable. It reduces manual effort, catches bugs early, and ensures consistent results across platforms. By integrating tools like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, or CircleCI with testing frameworks such as Jest or pytest, teams can build efficient workflows that save time and improve code quality.
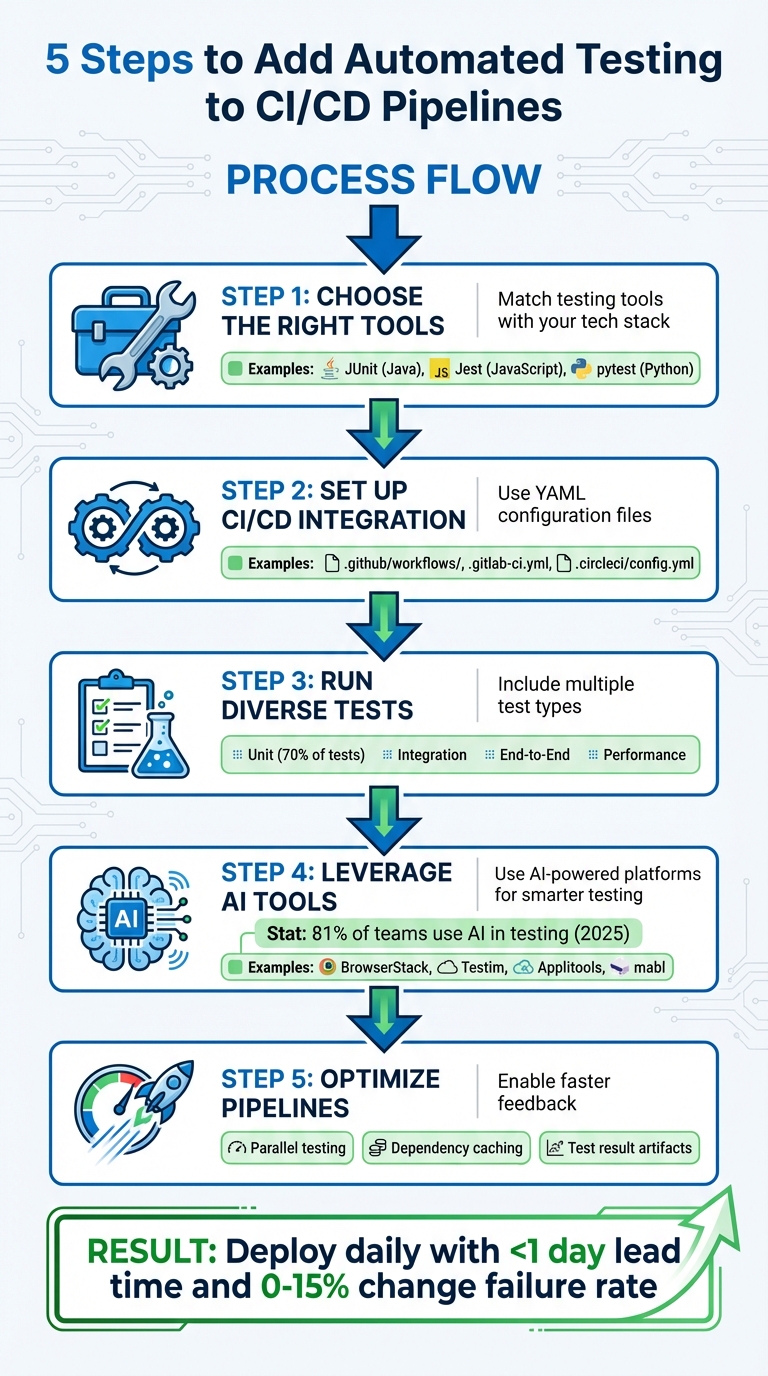
Here’s how you can get started:
- Choose the right tools: Match testing tools with your tech stack (e.g., JUnit for Java, Jest for JavaScript).
- Set up CI/CD integration: Use YAML configuration files (e.g.,
.github/workflows/) to define test steps and triggers. - Run diverse tests: Include unit, integration, end-to-end, and performance tests for thorough coverage.
- Leverage AI tools: Use AI-powered platforms like BrowserStack or Testim for smarter, adaptive testing.
- Optimize pipelines: Enable parallel testing, dependency caching, and test result artefacts for faster feedback.
Automated testing ensures your pipeline is efficient, scalable, and ready for frequent deployments. With the right setup, you can maintain high-quality code while reducing testing time dramatically.
5-Step Guide to Adding Automated Testing to CI/CD Pipelines
CI/CD Tutorial using GitHub Actions – Automated Testing & Automated Deployments
Selecting Tools and Technologies
When choosing testing tools, make sure they align with your team’s current tech stack and workflow. The tools should support the programming languages your team already uses. For example, Java teams often turn to JUnit, Python developers prefer pytest, and JavaScript teams typically rely on Jest. This compatibility helps your team write and maintain tests without needing to learn completely new frameworks.
Integration with CI/CD pipelines is just as important. Platforms like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI come with pre-built actions, such as code quality analysers for languages like Java, JavaScript, and Apex. Bernat Nosas Comerma, Lead of Global DevOps at Amplifon, shared why his team chose GitHub Actions:
"There are many ways to automate tests, but using Actions allows us to fully integrate our tests with GitHub events, which has enabled us to create some elaborate CI/CD strategies".
Scalability is another key consideration. Look for tools that support parallel testing and dependency caching. Your decision between hosted and self-hosted runners will also impact scalability. Comerma explains:
"We generally prefer GitHub-hosted runners because they’re powerful, convenient, and easy to use… But self-hosted runners let us test our software on custom hardware, which is critical for us to have clean, performant, and bug-free code".
For teams needing extensive cross-platform testing, cloud-based solutions like BrowserStack provide access to over 3,500 real devices and browsers. Once you’ve identified the tools, it’s time to explore how they work with leading CI/CD platforms and testing frameworks.
CI/CD Platforms and Testing Frameworks
After selecting tools, the next step is ensuring smooth integration between testing frameworks and CI/CD platforms. Jenkins remains a popular choice due to its flexibility and extensive plugin library. GitHub Actions offers seamless integration with version control workflows. GitLab CI and CircleCI also stand out, with features like orbs (CircleCI) and marketplace actions (GitHub) that simplify adding third-party tools like Cypress, Sauce Labs, and LambdaTest.
Your testing framework should cover multiple layers of testing. Start with unit tests, which are fast and catch issues early. Integration tests ensure that different components work together, while end-to-end tests simulate real user workflows. The key is selecting frameworks that integrate well with your CI/CD platform and support your tech stack.
How to Evaluate Testing Tools
Begin by checking whether the tools are compatible with your existing infrastructure, including cloud-hosted runners. Consider the learning curve – your team should be able to write, update, and debug test scripts efficiently. Community support is also crucial. A strong, active community means better documentation, more plugins, and quicker troubleshooting.
Fast and accurate feedback is critical for CI/CD success. Prioritise tools that provide clear logs, dashboards, and visual results – such as screenshots or videos – to help developers quickly identify and fix issues. Additionally, many modern platforms offer analytics for flaky tests (those that fail randomly without code changes), helping you address bottlenecks before they disrupt your pipeline. Features like test splitting and re-running only failed tests can also save significant time. Beyond traditional tools, AI-powered platforms are making automation smarter and more efficient.
Using AI-Powered Testing Tools
AI-driven testing tools are transforming automation workflows. By late 2025, 81% of development teams had incorporated AI into their testing processes. These tools often include self-healing capabilities, which automatically detect UI changes and update test scripts, reducing the time spent on maintenance.
AI tools go beyond maintenance. They can analyse test failures to identify whether the problem lies in the environment, the automation itself, or actual product regressions. Some platforms even use predictive test selection, running only the tests impacted by specific code changes to speed up pipelines. One organisation reported saving $1,000,000 annually by replacing thousands of manual assertion lines with AI-powered visual checkpoints. Tools like Testim, BrowserStack, Applitools, and mabl are particularly effective in addressing test flakiness and visual regressions.
How to Set Up Automated Testing in Your CI/CD Pipeline
Setting Up Your CI/CD Environment
Start by creating a YAML configuration file (like .github/workflows/, .gitlab-ci.yml, or .circleci/config.yml) to outline your pipeline’s stages, jobs, and test scripts. This file acts as the blueprint for your CI/CD process.
Next, provision runners to execute the tests. You can choose cloud-hosted runners from platforms like GitHub or GitLab for convenience, or set up self-hosted runners on your own machines if you require a more tailored environment. For security, store sensitive information as CI/CD variables or secrets instead of embedding them directly in your code. Finally, set up a test environment that closely resembles your production setup to ensure reliable results.
Creating the Test Environment
Using Docker containers is an excellent way to create isolated and reproducible test environments. You can specify Docker images such as node:16, python:3.12, or mcr.microsoft.com/playwright to match your project’s requirements. To speed up builds, implement caching for dependencies like node_modules or pip packages. As Tony Kelly puts it:
"Containers eliminate the ‘it works on my machine’ problem by ensuring that applications run the same in development, testing, and production environments".
For lean, production-ready images, multi-stage Docker builds are a smart choice. If you’re unsure where to start, tools like docker init can automatically generate a Dockerfile with reasonable defaults tailored to your platform.
Running Tests Automatically
Automate your pipeline to trigger on specific events, such as code pushes, pull requests, or scheduled intervals. Include commands like npm test, pytest, or npx playwright test in your job steps to run your test suites. To maintain code quality, set up version control status checks that block pull requests from being merged until all required tests pass.
Consider running quick checks, like linting or unit tests, before moving on to more resource-heavy tests. Use matrix builds to run tests in parallel across multiple operating systems (e.g., Linux, macOS, Windows) and browser engines (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit). This approach accelerates feedback loops and supports faster development cycles. Additionally, configure your pipeline to upload test reports, screenshots, and videos as artefacts whenever tests fail. This makes debugging easier and more efficient.
sbb-itb-fd1fcab
Adding Different Types of Tests
Incorporating a variety of tests into your CI/CD pipeline is essential for detecting issues early and ensuring smooth functionality across the board.
Unit and Integration Testing
Unit tests are the backbone of any testing suite, typically making up about 70% of the total tests. These tests focus on verifying individual sections of code during the build process, helping to catch issues early. Aim for at least 80% code coverage to block problematic commits. To automate this, configure your YAML file to run commands like npm test or pytest with every commit.
Integration tests, on the other hand, ensure that different services interact correctly. These tests usually run during the staging phase . For accuracy, execute them in environments that closely mimic production, using mocked datasets and service containers . To uphold code quality, require all tests to pass and enforce branch protection rules.
To keep your pipeline efficient, use parallel execution and test-splitting to speed up the process. Store test results as artefacts (e.g., using store_test_results) so your team can quickly review logs and stack traces when failures occur. Once these foundational tests are solid, the focus can shift to validating complete user experiences.
End-to-End and Performance Testing
End-to-end (E2E) tests are fewer in number but cover critical user workflows . These tests should run automatically on pull requests for key branches. To save time, leverage cloud-hosted browser grids with parallel workers (e.g., Microsoft Playwright Testing across 20+ workers).
Performance tests, meanwhile, assess how well your system handles different levels of user load. These tests are crucial for identifying potential slowdowns under heavy traffic. Before running resource-intensive E2E and performance tests, trigger lightweight checks to ensure the environment is ready. Use tools like Docker or infrastructure-as-code to replicate production-like conditions . As Virtuoso QA notes:
"Automation transforms E2E testing from a bottleneck into an accelerator of software delivery".
To improve debugging, make sure your pipeline captures detailed logs, screenshots, and even video recordings when tests fail. Most cloud services retain these artefacts for up to 90 days. Monitor flaky tests – those that fail inconsistently – and remove them to boost team confidence . You might also explore AI-driven testing tools that adapt to UI changes automatically, potentially cutting manual maintenance by 85%. After thorough pre-deployment testing, continue to check quality by testing in production.
Testing After Deployment
Post-deployment testing is just as critical. Synthetic monitoring involves running automated tests at regular intervals against production endpoints. These tests simulate user interactions and are particularly useful for high-value workflows like login and checkout processes. Canary testing takes a cautious approach by deploying updates to a small subset of servers or a single region first. This limits the impact of any issues before a full rollout.
Real User Monitoring (RUM) complements synthetic tests by collecting telemetry from actual user sessions. This data helps identify frontend errors and latency problems that automated tests might miss. Additionally, Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tools can be integrated with your pipeline to trigger automatic rollbacks if performance metrics fall below acceptable levels. Set up alerts based on Service Level Objectives (SLOs) to notify your team immediately when production quality takes a hit. As GitLab puts it:
"CI/CD is a continuous method of software development, where you continuously build, test, deploy, and monitor iterative code changes".
Best Practices for Long-Term Success
Automated tests are just the starting point; achieving long-term reliability requires consistent attention and prioritization of maintenance.
Focusing on Critical Test Coverage
Not every test deserves the same level of focus. Using the test pyramid approach can help you catch smaller issues early before they grow into bigger problems. Running your most predictive tests first in the pipeline is a smart way to identify issues quickly and minimize disruptions for developers. Save resource-heavy end-to-end tests for critical user journeys that could block deployments. As GitLab emphasizes:
"If a test can’t reliably block a merge, deployment, or release, it shouldn’t exist. Fix it or delete it."
Teams that adopt this mindset often see a change failure rate between 0–15% and can restore services in under an hour. This enables them to deploy daily with a lead time of less than a day. The key is to prioritize automation for workflows that bring the most value, instead of attempting to automate everything at once. This approach creates a solid foundation for smooth maintenance and collaboration.
Keeping Test Scripts Updated
As your application evolves, so should your automated tests. Regularly revising test scripts and data is essential. Use version control to manage these updates and schedule periodic reviews to clean out outdated test cases. Address flaky tests immediately by identifying unstable environments or unreliable data. BrowserStack highlights this necessity:
"Automated tests require continuous updates as your application changes. It is important to revise tests to cover new features and remove those that no longer contribute meaningful value."
Additionally, leverage test analytics to identify tests with low success rates or long execution times. Write modular, well-documented code that follows SOLID principles, and ensure your pipeline blocks merges into critical branches unless all automated checks pass.
Working with Workflow Automation Experts
Scaling automated testing efficiently often requires expert guidance. Specialists can assist with tool selection, performance optimization, and infrastructure management, ensuring your CI/CD pipeline operates at peak efficiency. By building on strong test coverage and timely updates, experts can help streamline processes. For example, Digital Fractal Technologies Inc. (https://digitalfractal.com) designs test pyramids tailored to business needs and employs advanced techniques like parallel testing, build caching, and containerization. They also monitor DORA metrics – deployment frequency, lead time for changes, change failure rate, and mean time to recovery – to provide actionable insights for continuous improvement.
In 2025, ITS collaborated with the mabl platform to achieve 95% test automation coverage. Under the leadership of VP Samar Khan, the team completed in just four months what would have taken two years with traditional tools like Selenium, cutting costs by 80%. Similarly, a SaaS company using GitLab CI reduced its time-to-market by 50% and enabled multiple daily deployments. Partnering with automation experts also facilitates the adoption of Infrastructure as Code (IaC), ensuring consistent environments and integrating security checks early in the pipeline .
Conclusion
To seamlessly incorporate automated testing into your CI/CD pipeline, start by selecting tools that align with your needs, defining well-rounded test cases like unit, integration, and end-to-end tests, and properly configuring YAML files (e.g., .gitlab-ci.yml or .circleci/config.yml). This process ensures code quality is validated before deployment, reducing the chances of release-related issues.
Atlassian’s Sten Pittet highlights the importance of fostering a "green build" culture, where teams address broken builds immediately. Coupled with daily code integration, this practice not only prevents technical debt from piling up but also ensures your codebase remains ready for deployment at all times. Teams adopting these habits often achieve lead times of less than a day and can recover from failures in under an hour. Such discipline lays the groundwork for ongoing improvements to your pipeline.
For long-term success, continuous refinement is key. Keep a close eye on test results, address flaky tests promptly, and refactor test suites as needed to maintain both speed and relevance. With developers already dedicating between 35% and 50% of their time to testing, debugging, and validation, a well-maintained automation setup can significantly ease this workload and help prevent burnout.
Expert guidance can further streamline pipeline optimization. Specialists can craft custom pipelines, implement advanced strategies like canary releases, and integrate security checks early in the development process. As Ajay Singh from Compunnel puts it:
"Automated testing is the cornerstone of every CI/CD pipeline… it lessens the amount of manual intervention required and most importantly detects issues before production deployment".
To stay focused on innovation while maintaining a reliable and scalable pipeline, consider partnering with workflow automation experts like Digital Fractal Technologies Inc. Their expertise can help you achieve a balance between efficiency and innovation.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of adding automated testing to a CI/CD pipeline?
Integrating automated testing into a CI/CD pipeline brings several advantages that can transform the development process. For starters, it offers faster feedback, catching issues early in the development cycle. This means bugs can be fixed promptly, leading to improved code quality and more dependable software releases.
Another major perk is the reduction in manual effort. By automating testing, teams can speed up delivery timelines without sacrificing consistency. On top of that, automated testing provides detailed insights that drive continuous improvement, helping organizations refine their development and deployment workflows over time.
How do AI-powered testing tools improve the efficiency of a CI/CD pipeline?
AI-powered testing tools simplify your CI/CD pipeline by automating the creation, execution, and upkeep of tests, cutting down on repetitive manual work. This means quicker feedback on code changes, enabling teams to resolve issues faster and keep projects on track.
These tools can also focus on high-priority tests, adjust to changing codebases, and clear out test backlogs, leading to a smoother and more efficient development process. With AI in the mix, your pipeline becomes stronger and more adaptable, boosting both productivity and the quality of your software.
How can I create a test environment that closely matches production in my CI/CD pipeline?
To create a test environment that closely resembles your production setup, start by using the same Docker images and configurations as your live environment. Make sure to pull the exact image tags and replicate runtime, library, and operating system versions. Tools like Testcontainers can be invaluable for spinning up dependent services – such as databases or message brokers – with configurations that match those in production.
In your CI pipeline, load the same environment variables and use either sanitized production data or realistic seed data for testing purposes. Run integration or end-to-end tests directly within the pipeline to verify that all services start correctly and to catch any issues early in the process. Once testing is complete, automate the cleanup of containers and other resources to keep your environment tidy. By following these steps, you can ensure your tests are reliable and reflect real-world conditions, helping you deliver high-quality software.

